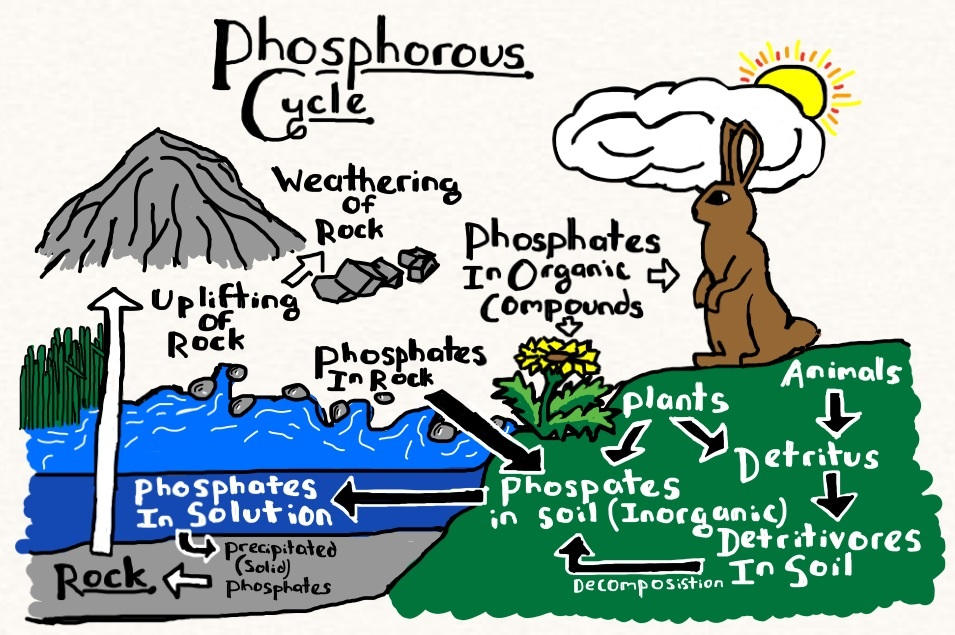
In March 2024, I attended the webinar Alternative circular fertilizers organised by Naturland. The aim was to understand how to improve resource efficiency by promoting alternative fertilisers. I learned that Phosphorus is a limiting factor in plant yield, meaning that crops cannot survive in absence of phosphorus as a nutrient. As a non-renewable resource, its loss would have major consequences on our food system.
Ali Aboukila, who works at Greentile, gives us insights on the importance of phosphorus in agriculture as well as its socio-environmental challenges. Interview with the agronomist.
1- What makes Phosphorus particularly important in agricultural ecosystems?
Ali Aboukila: Phosphorus is a major nutrient required for plant growth and development. It plays a crucial role in energy metabolism, membranes, structural support, genetic components, and photosynthesis processes. The low concentration and solubility of phosphorus in the soil make it a key growth-limiting factor for plant growth nearly everywhere on Earth.
2- How does it contribute to crop growth and soil health?
A.A: Firstly, it is essential for the photosynthesis process, which is the foundation of plant growth and development. Phosphorus- containing compounds are vital in energy metabolism, including ADP and ATP, which are the primary energy carriers in cells.
Secondly, phosphorus is a structural component of membranes, teeth, bones, and genetic components (DNA, RNA) in plants and animals.
Thirdly, phosphorus is crucial for the growth and development of plants, including root growth, shoot growth, and flowering. In agricultural ecosystems, phosphorus is often added to the soil through the application of chemical phosphate fertilizers to increase crop growth and yield.
However, the intensive use of P fertilizer has led to concerns about the environmental impact of phosphorus pollution, particularly in water bodies. Therefore, sustainable phosphorus management in agriculture is critical for maintaining crop growth and soil health while minimizing environmental impacts.
3- Where are the primary sources of Phosphorus found globally, and how accessible are these sources for agricultural use?
A.A: Phosphorus is primarily found in rock, particularly the mineral apatite, and is released into the environment through the weathering of rock minerals to produce free or weakly bound phosphate ions within aqueous solutions.
Organic phosphorus can also be found in living and decaying plant and animal tissues, as well as in highly-decomposed organic matter such as humus or with recently added poorly- decomposed materials such as crop residues.
In agricultural ecosystems, the primary sources of phosphorus are fertilizers and livestock manure. Fertilizers are derived from phosphate rock, which is mined and processed to produce phosphate fertilizers. China has the major sources of phosphate in Asia, and Australia has a significant source in Oceania, although its production is currently limited. Morrocco is the big player in Africa.
4- What factors contribute to the vulnerability of Phosphorus supply?
A.A: Phosphorus supply vulnerability is influenced by several factors, including physical, geopolitical, and socio-economic factors.
“Six countries control more than 90% of the world’s phosphorus resources“
- Physical factors include the geographic concentration of phosphorus resources, with six countries controlling more than 90% of the world’s resources, including Morocco, China, Algeria, Syria, Jordan, and South Africa. The distribution of phosphorus reserves is uneven, with some countries having large reserves while others are almost completely dependent on imported phosphorus for their agriculture.
Additionally, the estimates of phosphorus reserves are uncertain, and even in the most optimistic projections, the phosphate resources will be depleted within a couple of hundred years.
“Morocco’s control of Western Sahara is a source of controversy and tension“
- Geopolitical factors also contribute to the vulnerability of phosphorus supply. The geographic concentration of phosphorus resources makes them a potential source of conflict and instability, particularly in regions where the political situation is uncertain or where there are disputes over territory. For example, Morocco’s control of Western Sahara, which contains significant phosphate reserves, is a source of controversy and tension.
“Socio-economic factors affect the ability of countries to adapt to changes in phosphorus supply and demand.“
- Socio-economic factors, such as international trade regulations, energy prices, eating customs, population, dependence on imports, food security, ownership and production of phosphate ore, infrastructure, soil fertility, and distribution of income, also contribute to the vulnerability of phosphorus supply. These factors can affect the availability, accessibility, and affordability of phosphorus resources, as well as the ability of countries to adapt to changes in phosphorus supply and demand.
5- What are the key socio-political and environmental dangers resulting from the mismanagement of phosphorus in agricultural practices?
A.A:
- Socio-Economic Impacts: Mismanagement of phosphorus can lead to significant economic consequences, as seen in the recent >400% increase in phosphorus commodity prices due to factors like geopolitical disputes, trade wars, and escalating fuel prices. This can contribute to food crises and impact food security globally.
- Environmental Pollution: Inadequate phosphorus management can result in phosphorus losses to freshwaters through inappropriate fertilizer use and land management practices, posing a significant threat to water quality globally. This can lead to eutrophication, harmful algal blooms, biodiversity loss, oxygen-depleted “dead zones,” and contamination of drinking water supplies.
- Geopolitical Tensions: The geographic concentration of phosphorus resources in a few countries can create geopolitical tensions and conflicts, as seen in regions like Western Sahara, which holds significant phosphate reserves and is a source of controversy and instability.
- Resource Scarcity: The uneven distribution of phosphorus reserves and the uncertain estimates of phosphate rock reserves raise concerns about future scarcity and depletion of phosphorus resources, which could impact agricultural productivity and food security globally.
- Transboundary Nutrient Impacts: The international trade of food and non-food goods can create a novel transboundary context for nutrient impacts across aquatic ecosystems, highlighting the interconnectedness of phosphorus management on a global scale.
- Climate Change Risks: Mismanagement of phosphorus can exacerbate climate change risks, as the production and processing of phosphate rock are energy-intensive processes that contribute to environmental degradation and climate impacts.
6- What innovative strategies or technologies are being developed to address challenges related to Phosphorus management and utilisation in agriculture?
A.A:
- Biofertilizers:
Biofertilizers are microorganisms that can enhance the availability of phosphorus to plants by solubilizing or mobilizing phosphorus from insoluble sources. - Engineered plants:
Genetic engineering techniques can be used to develop plants with improved phosphorus use efficiency, such as plants with increased root uptake and transport of phosphorus, or plants that can tolerate low phosphorus availability in the soil. - Agricultural management practices:
Agronomic interventions such as band placement of fertilizers, conservation tillage, and use of cover crops can improve phosphorus use efficiencies in farming systems. - Sustainable phosphorus management:
Sustainable phosphorus management is essential for global food security and the conservation of soil and water bodies. This can be achieved through the use of innovative techniques such as phosphorus recovery from wastewater, recycling of phosphorus-containing waste materials, and the development of new phosphorus fertilizers that have lower environmental impacts. - Phosphorus recycling:
Phosphorus recycling is an important strategy for reducing the dependence on non-renewable phosphorus resources and minimizing the environmental impacts of phosphorus fertilizer use. This can be achieved through the recovery of phosphorus from wastewater, animal manure, and other waste materials. - Precision agriculture:
Precision agriculture techniques can be used to optimize phosphorus fertilizer application rates and timing, reducing phosphorus losses and improving crop yields. - Integrated nutrient management:
Integrated nutrient management strategies can be used to optimize the use of all nutrients, including phosphorus, in agricultural systems, reducing the need for external inputs and minimizing environmental impacts.
7- How feasible is the recycling of Phosphorus, and what practices are currently employed?
A.A: The feasibility of phosphorus recycling is high, given the availability of phosphorus waste streams, particularly in the form of manure and wastewater, which can be used as a sustainable source of phosphorus for the world over.
Current research is focused on the recycling of phosphorus from waste streams, which is expected to be the cornerstone of maintaining food security for a growing global population.
Phosphorus recycling from manure is a promising solution to our disappearing phosphorus resources. In the Netherlands, the main losses of phosphorus in the food sector are through sewage sludge, other wastewater, and food waste. Phosphorus in manure is almost completely recycled on arable and pastureland. However, losses from the fields or from stables are relatively minor, although they have a high environmental impact. In the whole wastewater treatment sector, only 0.2 Mt P from the 13.1 is recovered, and the rest is going to landfill and cement (80%) and water (20%).
Granulation is a key technology in recycling phosphorus. It is used to transform organic materials, including manure, into a dry, market-ready granular product.
In the case of manure, granulation works by taking the nutrient-rich cake left over from the anaerobic digestion process and using wet granulation (tumble-growth agglomeration or “pelletizing”) to process it into a granular product, which is then dried and cooled. The resulting product is nearly odor-free and goes beyond EPA qualifications for a Class A Biosolid, quelling many of the worries associated with the issues surrounding the traditional method of land-applying raw material.
Granulation mitigates many of the issues associated with raw manure, such as difficult handling, high transportation costs, and challenges in managing nutrients. Granulation produces a marketable product and offers ample opportunity for product customization, offering a premium product where waste management costs were previously incurred. Furthermore, a granular product helps to reduce opportunity for nutrient runoff, because no additional moisture is being added to soil upon application.
8- What initiatives or campaigns have proven effective in raising awareness about the importance of sustainable Phosphorus management, and how can such efforts be scaled or replicated?
A.A:
- Sustainable Phosphorus Management: A Transdisciplinary Challenge:
This initiative, described in a 2024 report, involves a multi-stakeholder approach to sustainable phosphorus management, bringing together experts from various fields to develop a global transdisciplinary roadmap. - Roadmap Toward Phosphorus Sustainability:
This NC State University project aims to elevate phosphorus sustainability in the public consciousness, recognizing that successful awareness- raising is necessary to achieve sustainability goals. - Phosphorus Awareness Project (PAP):
The PAP is an education campaign by SERCUL that educates the general community about the impact of too many nutrients in the Swan and Canning Rivers in Western Australia. The project aims to raise awareness of the importance of sustainable phosphorus management and the impact of phosphorus pollution on water quality.
To scale or replicate these efforts, the following strategies can be employed:
- Collaboration and Partnership:
Collaboration between stakeholders, including governments, academic institutions, non-governmental organizations, and the private sector, can help to leverage resources and expertise to promote sustainable phosphorus management. - Education and Awareness-Raising:
Education and awareness-raising campaigns can help to inform the public and key stakeholders about the importance of sustainable phosphorus management, the challenges associated with phosphorus scarcity and pollution, and the potential solutions to these challenges. - Policy and Regulation:
Governments can play a critical role in promoting sustainable phosphorus management by implementing policies and regulations that incentivize sustainable practices, such as recycling and reuse, and discourage unsustainable practices, such as overuse and pollution. - Innovation and Technology:
Innovative technologies and practices can help to improve phosphorus use efficiency, reduce losses, and promote recycling and reuse. These technologies can be developed and promoted through research and development efforts, demonstration projects, and technology transfer programs. - Monitoring and Evaluation:
Monitoring and evaluation of phosphorus management practices can help to identify areas for improvement and ensure that sustainable practices are being implemented effectively. This can be achieved through the development and implementation of monitoring and evaluation frameworks, as well as the use of data and analytics to track progress and identify trends.
9- What actionable steps can individuals, farmers, or organizations take to contribute to sustainable Phosphorus management and conservation efforts?
A.A: Individuals, farmers, and organizations can take several actionable steps to contribute to sustainable phosphorus management and conservation efforts:
- Implement Efficient Fertilizer Practices:
Individuals and farmers can adopt precision agriculture techniques to optimize phosphorus fertilizer application rates, reducing waste and environmental impact. - Promote Soil Health:
Organizations can educate farmers on the importance of maintaining healthy soils through practices like cover cropping, reduced tillage, and organic matter additions, which can improve phosphorus availability and reduce the need for external inputs. - Adopt Nutrient Management Plans:
Farmers can develop and implement nutrient management plans that focus on optimizing phosphorus use efficiency, reducing losses, and promoting recycling of nutrients within the farm system. - Explore Phosphorus Recycling:
Organizations can invest in technologies for recycling phosphorus from waste streams, such as manure and wastewater, to reduce dependence on mined phosphates and minimize environmental pollution. - Support Research and Innovation:
Organizations can fund research initiatives focused on developing sustainable phosphorus management practices, technologies, and policies to address the challenges of phosphorus scarcity and pollution. - Advocate for Policy Changes:
Individuals and organizations can advocate for policies that incentivize sustainable phosphorus management practices, such as phosphorus recovery, recycling, and reuse, while discouraging unsustainable practices that contribute to environmental degradation. - Engage in Knowledge Sharing:
Farmers and organizations can participate in knowledge- sharing platforms, workshops, and training programs to exchange best practices and experiences related to sustainable phosphorus management.
By taking these actionable steps, individuals, farmers, and organizations can play a crucial role in contributing to sustainable phosphorus management and conservation efforts, ensuring the long-term availability of phosphorus for agricultural production while minimizing environmental impacts.